Based on meta-analyses and large multi-centre randomized controlled trials, standard neurofeedback training protocols have been found to be efficacious and specific for ADHD symptoms, and as effective as methylphenidate medication. Additionally, Neurofeedback has been shown to have long term effects. Studies have also shown it to be efficacious for sleep problems. Furthermore, Neurofeedback is considered an emerging and promising (possibly efficacious with potential) treatment for ASD symptoms, comparable to other interventions for ASD. However, as in all treatments, there is no guarantee that Neurofeedback will be successful for every individual.
Based on meta-analyses and large multi-centre randomized controlled trials, standard neurofeedback training protocols have been found to be efficacious and specific for ADHD symptoms, and as effective as methylphenidate medication. Additionally, Neurofeedback has been shown to have long term effects. Studies have also shown it to be efficacious for sleep problems. Furthermore, Neurofeedback is considered an emerging and promising (possibly efficacious with potential) treatment for ASD symptoms, comparable to other interventions for ASD. However, as in all treatments, there is no guarantee that Neurofeedback will be successful for every individual.
Neurofeedback is an advanced intervention that presents the participant with real-time feedback on brainwave activity, as measured by sensors on the scalp, and typically in the form of visual or audio rewards. When the brain activity changes in the direction desired by the neurofeedback protocol, a positive ‘reward’ feedback is given to the individual. Neurofeedback uses operant conditioning for self-regulation of symptoms.
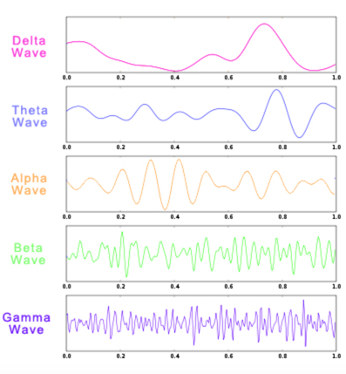
Neurofeedback works by training up or down certain brain wave frequencies. More efficient and effective brain wave patterns make the brain function more effectively and reduce problematic symptoms. To improve the chances of success from Neurofeedback training, Quantitative Electroencephalography (QEEG) investigation should be done before the Neurofeedback program is planned.